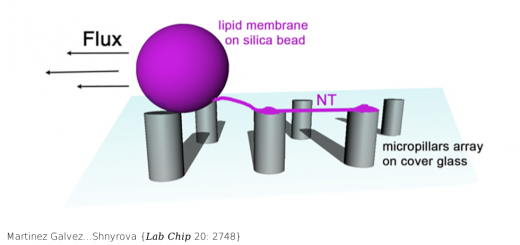
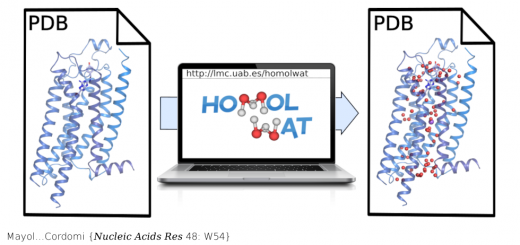
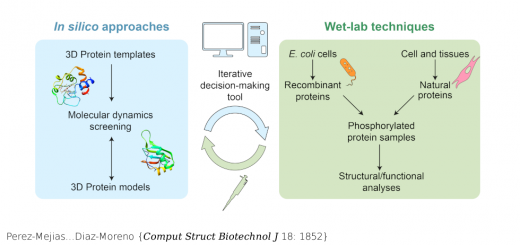
Marine n-3 PUFAs modulate IKs gating, channel expression, and location in membrane microdomains
Moreno C, de la Cruz A, Oliveras A, Kharche SR, Guizy M, Comes N, Starý T, Ronchi C, Rocchetti M, Baró I, Loussouarn G, Zaza A, Severi S, Felipe A, Valenzuela C.
Cardiovasc Res. 2015 Feb.; 105: 223. [Epub 11 December 2014].
Polyunsaturated fatty n-3 acids (PUFAs) have been reported to exhibit antiarrhythmic properties. However, the mechanisms of action remain unclear. We studied the electrophysiological effects of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) on IKs, and on the expression and location of Kv7.1 and KCNE1. [… …] We provide evidence that acute application of PUFAs increases Kv7.1/KCNE1 through a probably direct effect, and shows antiarrhythmic efficacy under IKr block. Conversely, chronic EPA application modifies the channel activity through a change in the Kv7.1/KCNE1 voltage-dependence [….]
PubMed:
25497550.
Doi:
10.1093/cvr/cvu250
Related Work by the Authors