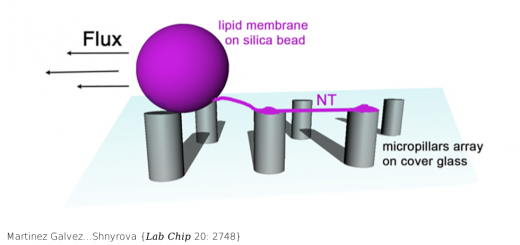
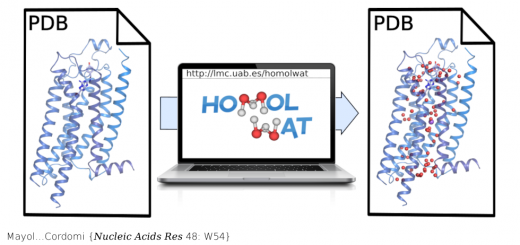
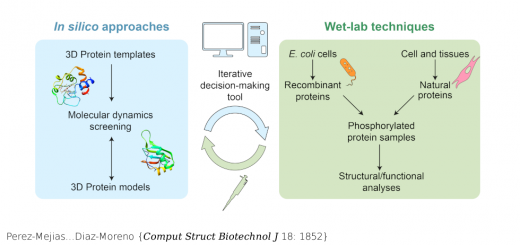
Allosterism and signal transfer in DNA

Secondary protein of allosteric couple binding to free and effector-bound DNA at different distances from BAMHI effector protein binding site. Signal transfer through DNA between the binding sites of the two proteins is achieved by transient propagation of structural fluctuations without change in the equilibrium structure of the DNA. Depending on the distance between the two binding regions, the signal phase can either favor or disfavor cooperativity through correlated atomic fluctuations and entropy penalty change.
Balaceanu A, Perez A, Dans PD, Orozco M.
Nucleic Acids Res 2018 Sep; 46: 7554.
We analysed the basic mechanisms of signal transmission in DNA and the origins of the allostery exhibited by systems such as the ternary complex BAMHI-DNA-GRDBD. We found that perturbation information generated by a primary protein binding event travels as a wave to distant regions of DNA following a hopping mechanism. However, such a structural perturbation is transient and does not lead to permanent changes in the DNA geometry and interaction properties at the secondary binding site. The BAMHI-DNA-GRDBD allosteric mechanism does not occur through any traditional models: direct (protein-protein), indirect (reorganization of the secondary site) readout or solvent-release. On the contrary, it is generated by a subtle and less common entropy-mediated mechanism, which might have an important role to explain other DNA-mediated cooperative effects.
PubMed: 29905860. Doi: 10.1093/nar/gky549. Free PMC article